A Systematic Random Sample Involves Which of the Following Activities
Then from each stratum or group a certain. Random sampling is a probability sampling technique is a method of choosing a sample of observations from a population to make assumptions about the population.

Four Types Of Random Sampling Techniques Explained With Visuals By Terence Shin Towards Data Science
Orton 2000 notes that in an archaeological setting some practitioners worry that a true simple random sample has the appearance of bunching and seek to avoid it.
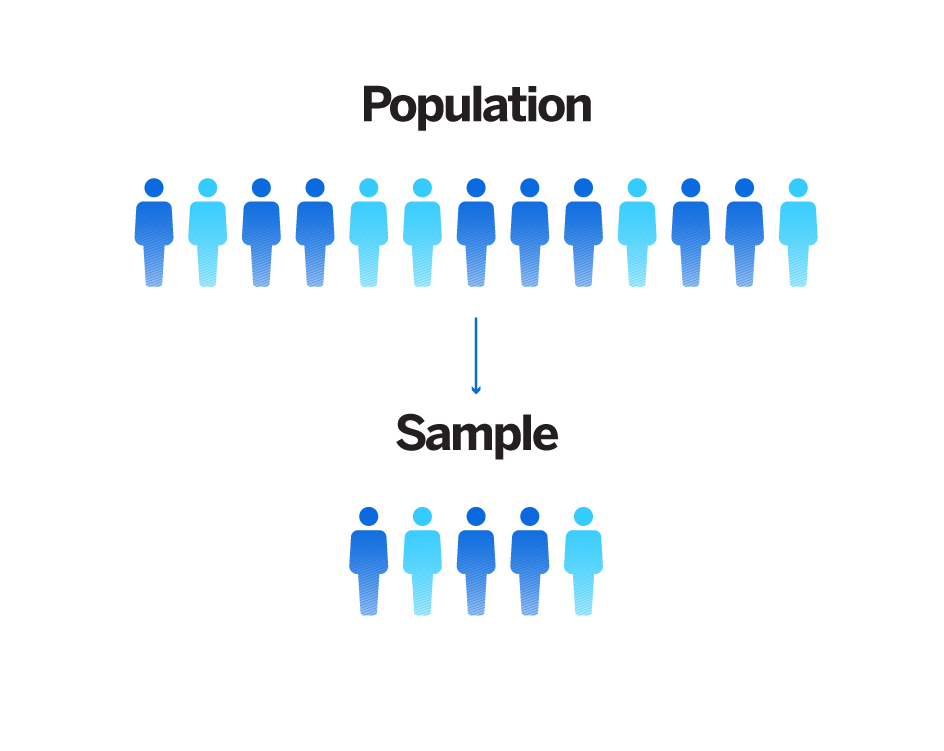
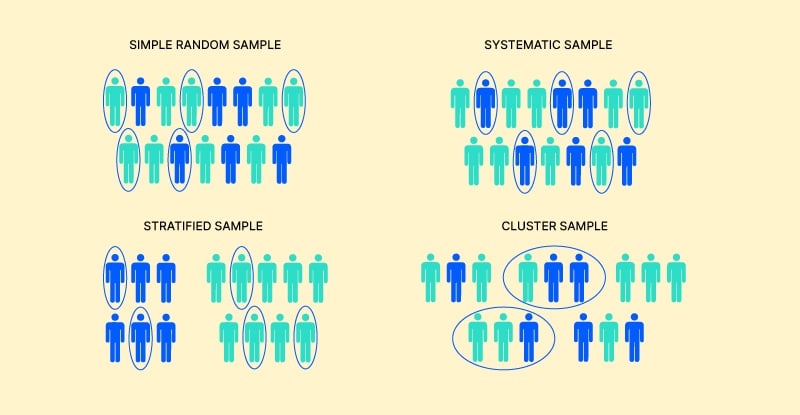
. Inna simple random sample if a population had 100 individuals the chance of any one individual being selected for the sample is. The following are the feature of a good sample. Simple random sampling is such that each possible sample of size n units has an equal chance of being selected.
Which of the following yields a systematic sample. Systematic sampling is the selection of specific individuals or members from an entire population. Which of the following is an advantage of systematic sampling over random number sampling.
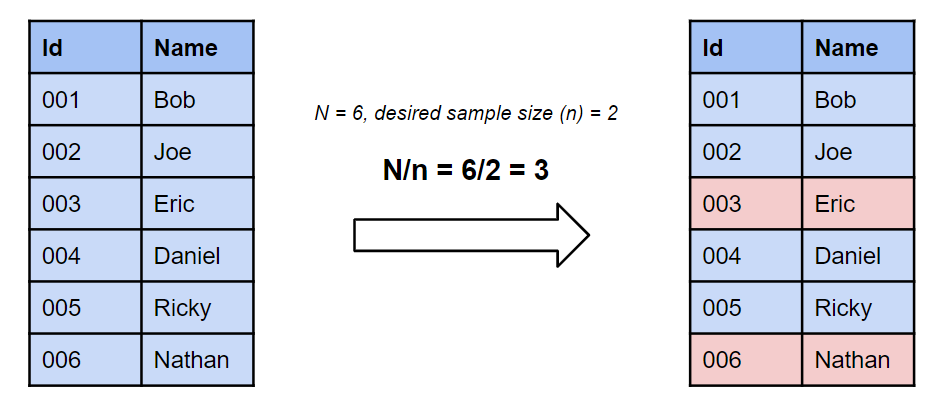
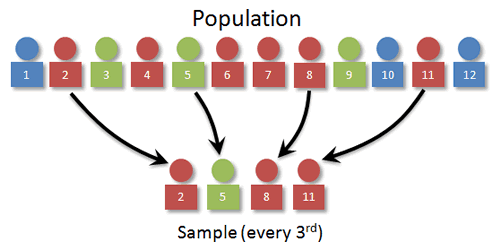
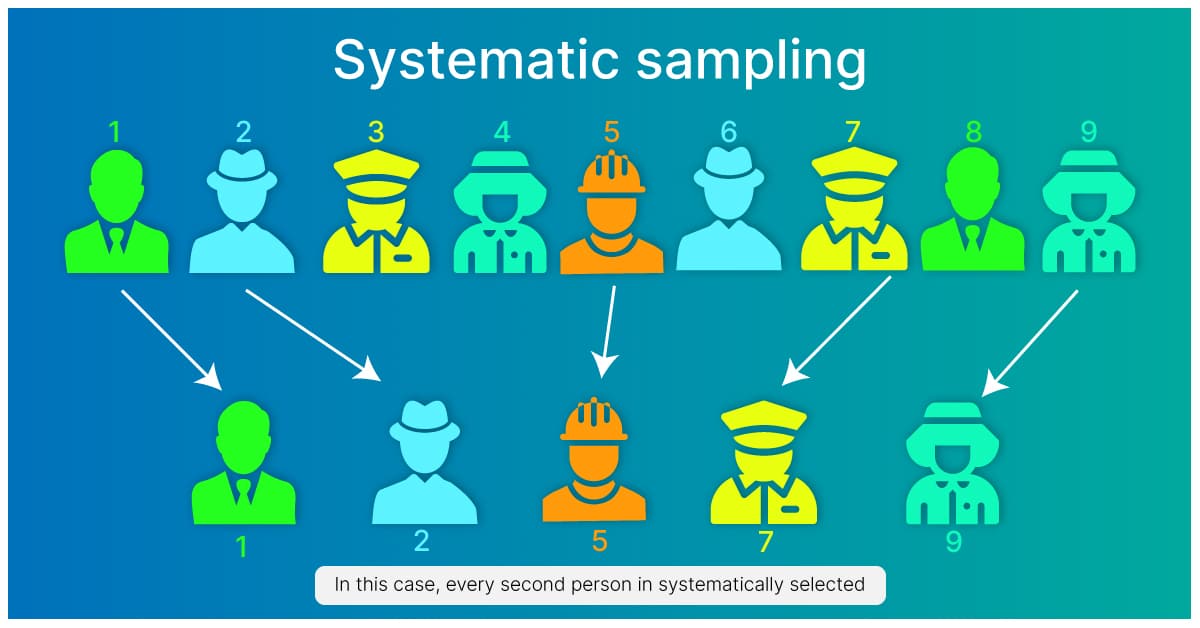
In selecting a sample of n units from a population of N units when Nnk using a systematic sampling approach we follow the following steps. Which of the following sampling techniques involves choosing individuals from the population at random where the proportions of members of different groups are the same in population and the sample. Systematic sampling is a type of probability sampling method in which sample members from a larger population are selected according to a random starting point but with a fixed periodic interval.
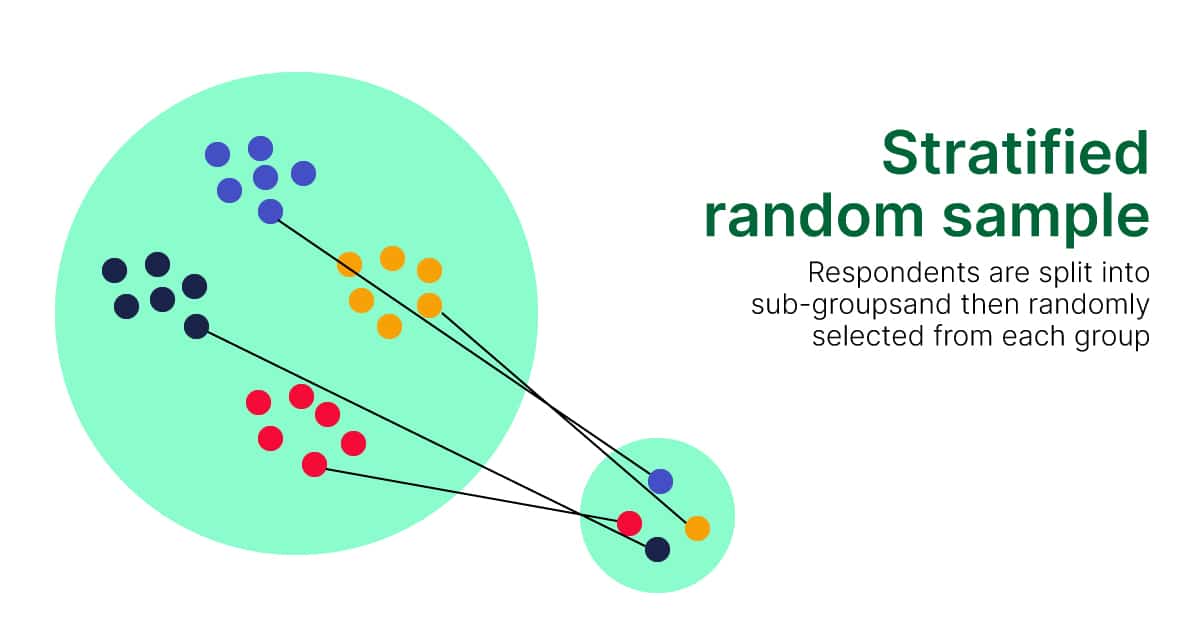
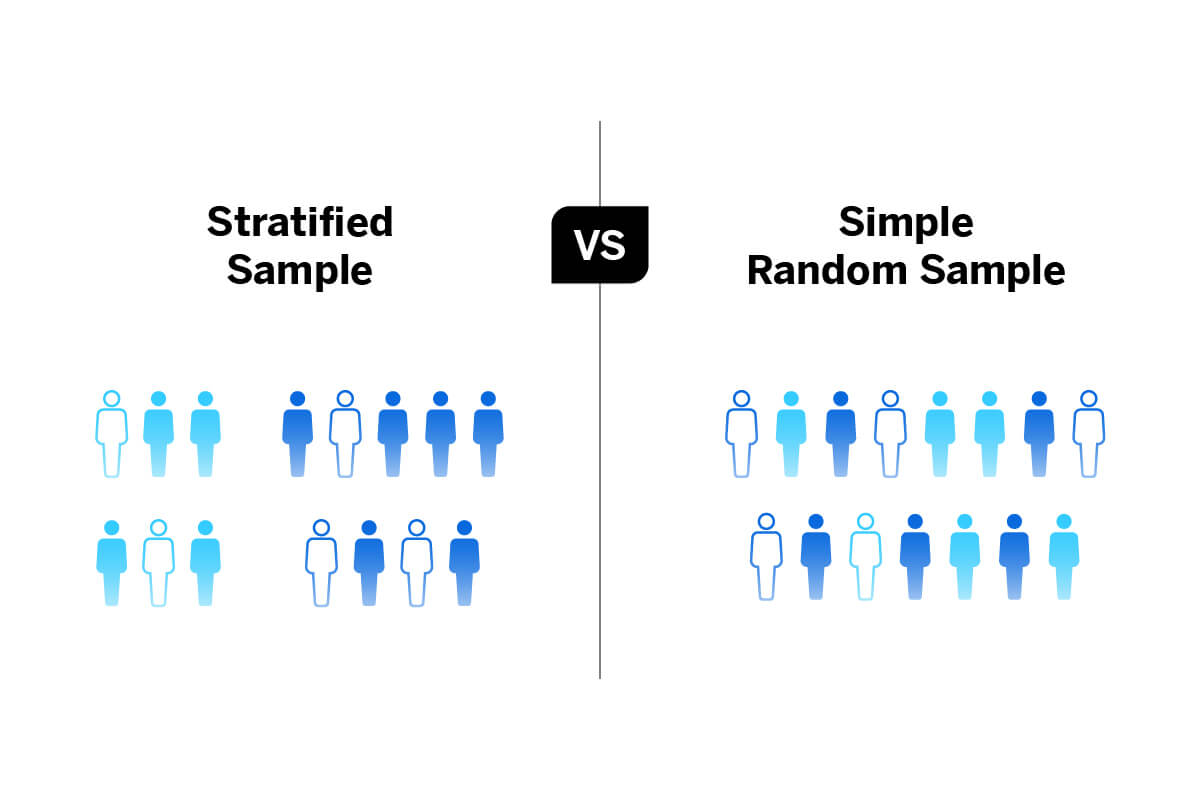
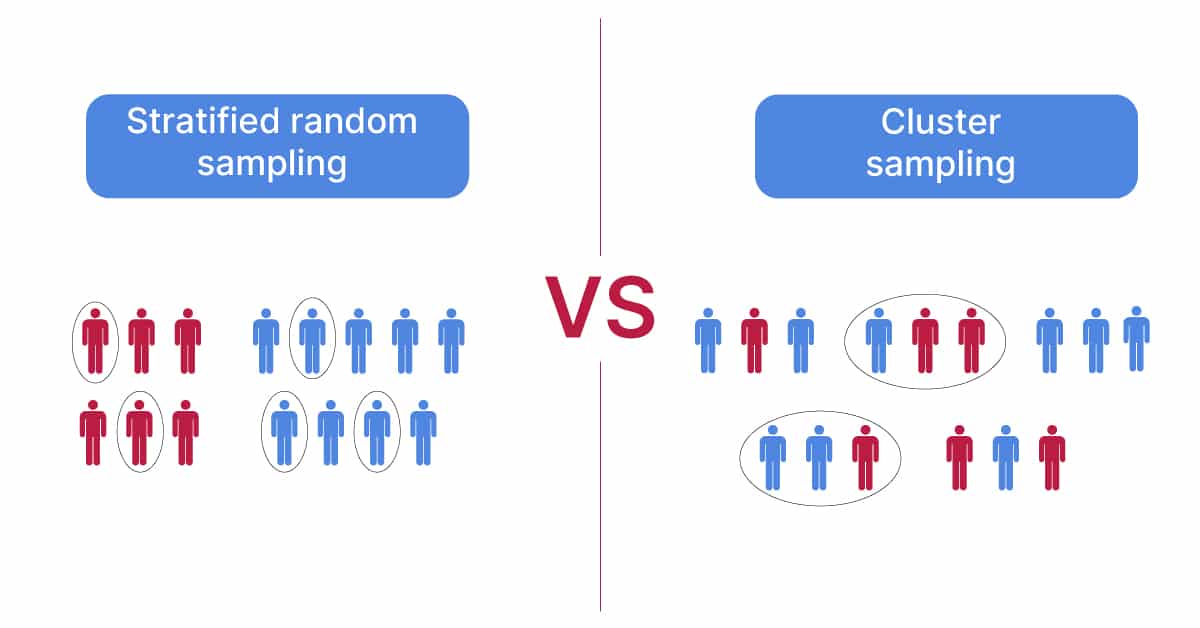
Lastly repeat the sampling interval to choose subsequent elements. First calculate and fix the sampling interval. Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves dividing a population into smaller groupscalled strata.
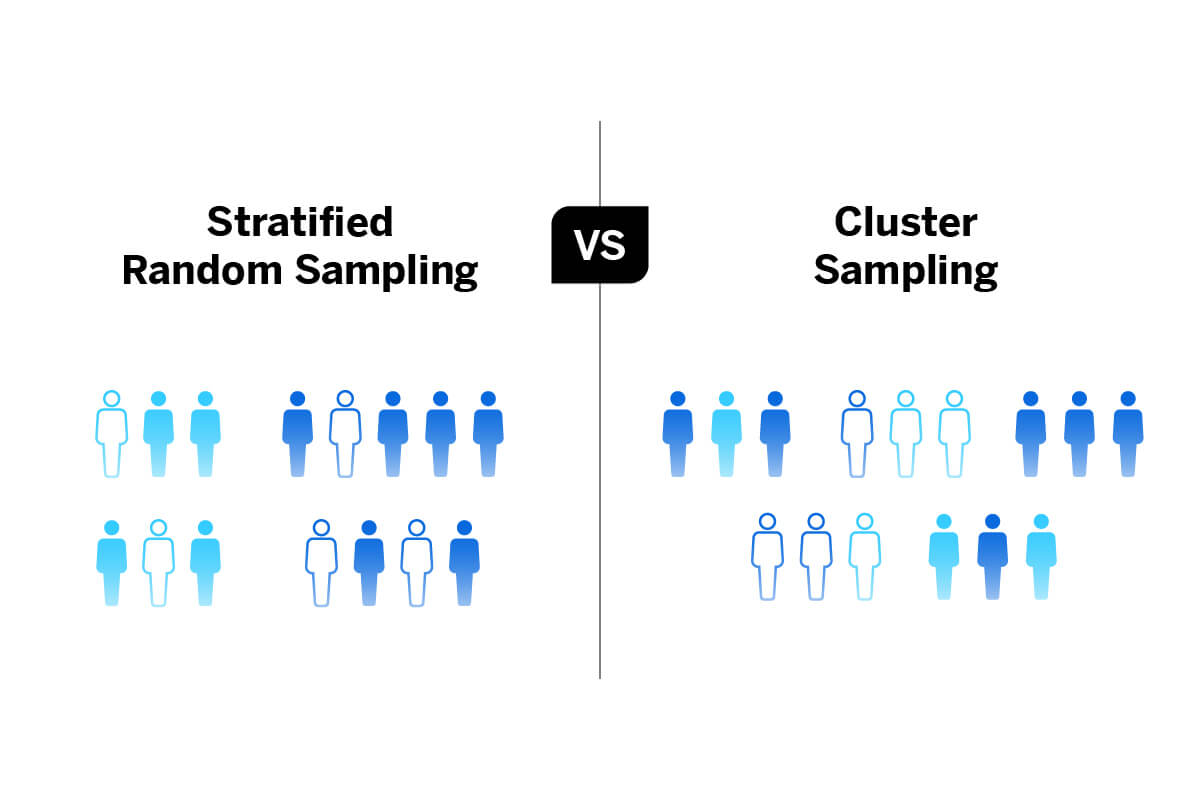
Selecting all items on a day or week. Probability sampling methods are of the following types a Simple Random Sampling Simple random sampling involves randomly selecting activities ie a sample from a larger set of activities ie the entire population. This type is sample involves dividing the population into different groups or strata and then picking samples from each stratum or group.
A sampling method in which the auditor selects a -group of contiguous items from within the population. A Stratified random sampling b Systematic sampling c Cluster or multistage sampling. A random sample of 8 is selected from the males and a separate random sample of 7 is drawn from the females.
In selecting a sample for attribute testing systematic selection involves which of the following approaches. The groups or strata are organized based on the shared characteristics. Systematic sampling is one way of doing so.
Determine the sampling interval k dividing TV by k Nn. Visit BYJUS to learn different types of random sampling with its formula and examples. The systematic sampling method is comparable to the simple random sampling method.
The non-probability method is a sampling method that involves a collection of feedback based on a researcher or statisticians sample selection capabilities and not on a fixed selection process. B All students in a class are grouped according to their gender. Each item in the population having an equal chance of selection.
Every nth item being selected after a random start. It provides a stronger basis for statistical conclusions. The selection often follows a predetermined interval k.
The number of elements in the population divided by the number of elements needed for the sample Choose a random starting point between 1 and the sampling interval. Select a random number between 1 and k Say this is r. List the units giving a serial number from 1 to N.
However it is less complicated to conduct. Asked Apr 10 2017 in Psychology by MrMiller. Systematic sampling involves randomly selecting the first item to sample and then selecting subsequent activities at regular intervals.
In some cases the population to be studied is too huge and diverse that it becomes difficult to conduct the research to study a specific behavior of the population. Cases following any systematic pattern. For example Lucas can give a survey to every.
Cluster sampling often involves selecting. It enables the auditor to use the more efficient sampling with replacement tables. Although proportionate stratified sampling involves selecting individuals from predetermined subgroups of the population it does not guarantee that each subgroup in the sample will have a large number of individuals.
A Stratified random sampling In this method the universe or the entire population is divided into strata ie a number of homogenous groups. In the population is a higher priority that a strictly random sample then it might be appropriate to choose samples nonrandomly. Q1 Briefly explain the following methodstechniques of restricted random.
Like simple random sampling systematic sampling is a type of probability sampling where each element in the population has. Systematic random sampling is the random sampling method that requires selecting samples based on a system of intervals in a numbered population. Below are the example steps to set up a systematic random sample.
A junior auditor has been assigned to audit bank and cash balances of XYZ Co. A A random sample of 15 students is selected from a class without replacement. Your first selected unit is r.
Goal Orientation - the sampling design should be based on the studys goals and objectives Measurability - the sampling design provides the data necessary for analysis enables valid inferences to be made about the population from the sample Practicality - the actual activities of sampling have been identified and are feasible. A sampling method in which the auditor selects items based on random numbers matched to items in population and each item has an equal chance of selection. An appropriate sampling interval should be chosen so that the company achieves the desired sample size.
In most situations the output of a survey conducted with a non-probable sample leads to skewed. In systematic random sampling the researcher randomly selects. An arbitrary selection with no conscious bias.
The first case and every kth case thereafter.
Probability Sampling What It Is How To Use It Qualtrics
Types Of Sampling Sampling Methods For Social Research Voxco

Sample Multiple Choice Questions
Voxco Guide To Sampling Methods And Types Voxco

Four Types Of Random Sampling Techniques Explained With Visuals By Terence Shin Towards Data Science

7 3 Probabilistic And Non Probabilistic Sampling Techniques Research Methods For The Social Sciences An Introduction
Four Types Of Random Sampling Techniques Explained With Visuals By Terence Shin Towards Data Science

Four Types Of Random Sampling Techniques Explained With Visuals By Terence Shin Towards Data Science

How To Use Stratified Random Sampling In 2022 Qualtrics
Sampling Techniques Themed Math Worksheets Ages 11 13

Systematic Sampling What Is Systematic Sampling By Anthony B Masters Medium
Qmss E Lessons Types Of Sampling
How To Use Stratified Random Sampling In 2022 Qualtrics

Systematic Random Samples Definition Formula Advantages Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Comments
Post a Comment